
A Digital Product Passport is an electronic record system designed to enable tracking and reliable verification of a product throughout its life cycle. This system can track the progress of the product from production, through the supply chain, to end-users and even the recycling process.
The Digital Product Passport ensures the product's authenticity and the reliability of the product's declared features. Additionally, it makes it possible to track the product's environmental impact and sustainability performance, thus enabling monitoring of the product's environmental impact.
The Digital Product Passport uses powerful encryption techniques such as blockchain technology to store all information related to the product in an encrypted form and makes this information accessible only to verified users. This makes it impossible to counterfeit or alter the product.
The Digital Product Passport is a technology designed to make products more sustainable. By providing traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain, it helps reduce the environmental impact of products during production, use, and recycling.
Why digital product passports?
Because the EU aims to lead the world in building a circular economy by reducing its carbon footprint and supporting sustainable production and consumption of goods/products and their parts, DPPs make sense. The regulation states that the product passport comprises “a set of data specific to a product that includes the information (specified in the delegated act) and that is accessible via electronic means through a data carrier”. The product passport will provide relevant product information, improved product traceability and supply chain visibility, better insight into compliance, and full-lifecycle tracking of substances of concern within the given product. These improvements underpin the creation of a circular economy and contribute to the overall EU circular economy action plan.
While manufacturers will be most directly affected by the EU digital product passport requirement, the regulation extends the responsibilities of and benefits to most parties within the value chain, from importers and distributors to recycle, repair, and maintenance professionals, from governments and other public or civil authorities to consumers and end-users.
The Digital Product Passport emerged to increase traceability of products throughout the supply chain and to measure sustainability performance.
Increasing social awareness of sustainability, as well as the widespread adoption of advanced technologies such as blockchain to provide traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain, played an important role in the emergence of the Digital Product Passport.
The implementation of digital product passports in these value chains is designed to support:
- Sustainable product production - enable the transition to circular economy and therefore boost material and energy efficiency, extend product lifetimes, and optimise product use.
- Businesses to create value through circular business models - thanks to the improved access to data with digital product passports, more businesses can implement service and repair based business models.
- Consumers to make more informed purchasing decisions - once they are provided with information on the total impact of their buying behaviours.
- Verify compliance with legal obligations - the digital product passport will also act as a record of the standards a product complies with and provides auditors with a data to evaluate this.
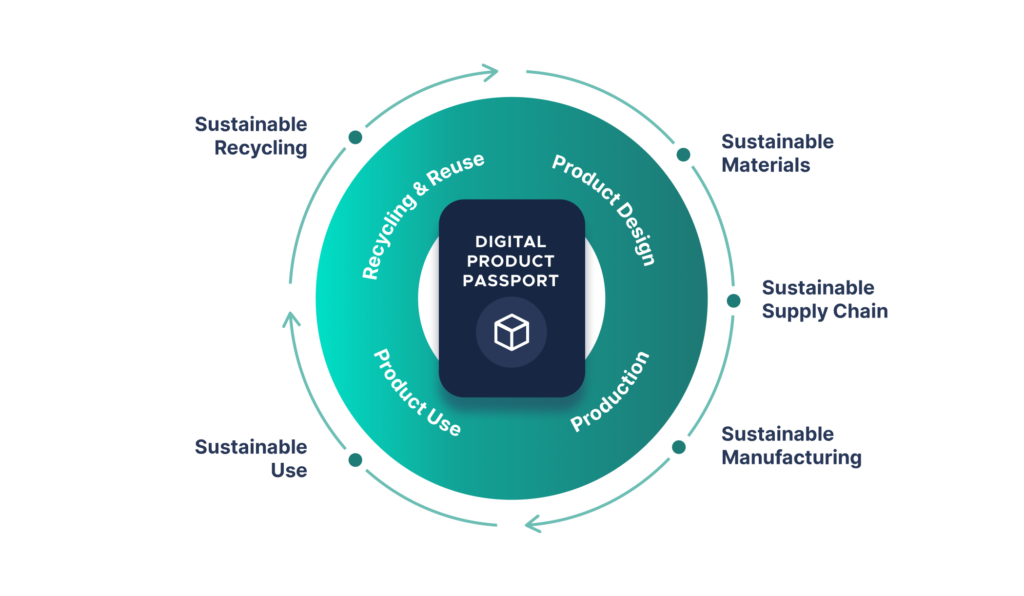
The Digital Product Passport provides an important solution in ensuring traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain, preventing counterfeit products, and measuring and reducing environmental impacts. Therefore, the Digital Product Passport is increasingly being used to support sustainability and ensure the reliability of products.
The sectors and products where the Digital Product Passport will be applied include: consumer electronics, batteries, ICT, fashion, furniture, as well as "high-impact intermediate products" such as steel, cement, and chemicals. The integration of the digital product passport into these sectors and products is expected to promote sustainable products, create new business opportunities among economic actors, assist consumers in making sustainable choices, and enable stakeholders to verify compliance with legal obligations, thus accelerating the transition to a circular economy.
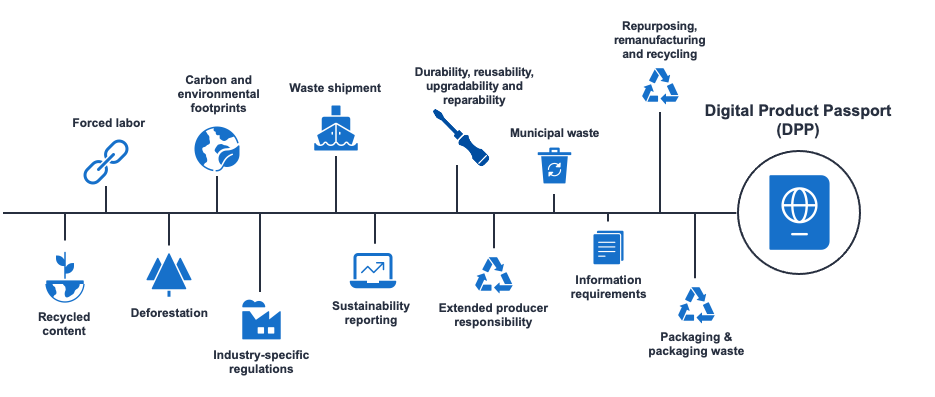
The practicalities of digital product passport implementation
From an operational perspective, it’s not as difficult as it may first seem. Once a framework is defined for the information to be included in digital product passports, traceability software can be used to standardise data sets coming from existing ERP systems. The required unique product identifiers can use existing technologies such as barcodes, QR codes, RFID tags, or similar, for digital product passport data submission. In the end, this process can be almost entirely automated.

